OSPF Flooding Filters in Hub-and-Spoke Environments
Technology Resources » OSPF Articles » OSPF Flooding Filters in Hub-and-Spoke Environments
The OSPF flood reduction functionality configured with the ip ospf database-filter all out interface configuration command can be used to reduce OSPF traffic and minimize the OSPF database size on small remote routers in hub-and-spoke environments.
The command stops all OSPF flooding over the selected interface and shall be used on a hub router in a hub-and-spoke network to stop the LSA flooding over the hub-to-spoke links. The flooding in the spoke-to-hub direction is not affected. The hub router and any other regular OSPF router in the network retain full visibility of the OSPF topology database, while the spoke router’s OSPF database contains only locally originated LSAs.
Since no LSAs are propagated from the hub router to the spoke routers, the spoke routers have to use a routing mechanism other than OSPF to reach the hub router. A static default route pointing to the hub router is usually used in environments where the spoke routers have a single upstream connection to the hub router.
Sample Network
The OSPF flood reduction is best illustrated with a sample hub-and-spoke network. A network with three spoke sites and a hub site (see the following figure) was used to generate the printouts.
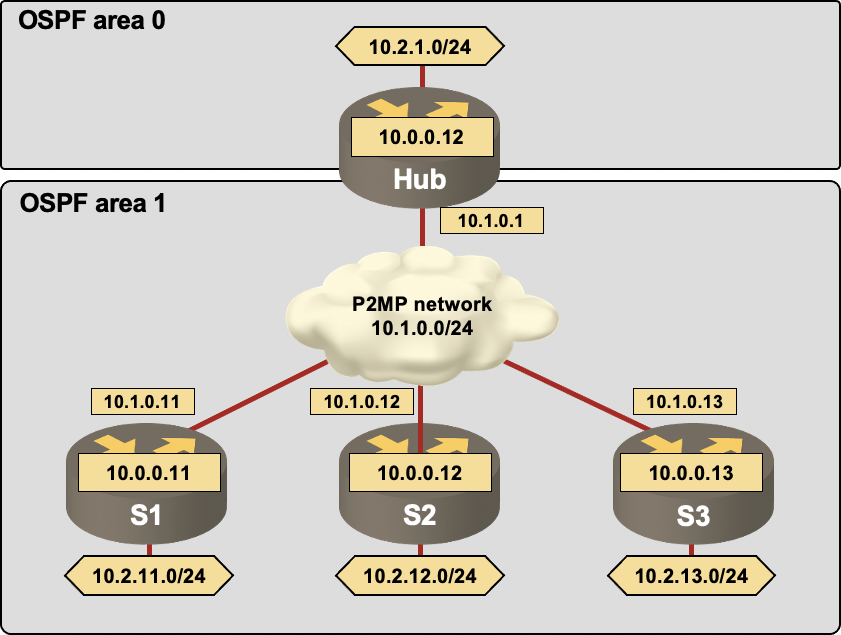
The topology and IP addressing of the sample network
Before the ip ospf database-filter all out command has been configured on the hub router, the OSPF database on the spoke routers contained all LSAs originated within the area (no out-of-area LSAs were originated by the hub router as the area 1 was configured with the area 1 nssa no-summary router configuration command on the hub router).
S1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (10.0.0.11) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
10.0.0.1 10.0.0.1 5 0x80000007 0x00129E 4
10.0.0.11 10.0.0.11 1671 0x80000003 0x00C06C 4
10.0.0.12 10.0.0.12 1562 0x80000003 0x002AFA 4
10.0.0.13 10.0.0.13 6 0x80000005 0x00839B 4
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
0.0.0.0 10.0.0.1 1607 0x80000001 0x00D852
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Tag
0.0.0.0 10.0.0.1 1742 0x80000001 0x00ACF9 0
10.3.1.0 10.0.0.12 1566 0x80000002 0x001447 0
Similarly, the IP routing table on the spoke routers contained all the routes within the area:
S1#sh ip route | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is 10.1.0.1 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 11 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.11/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.2.11.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
O 10.2.12.0/24 [110/129] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O 10.2.13.0/24 [110/129] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O 10.1.0.13/32 [110/128] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O 10.0.0.12/32 [110/129] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O 10.1.0.12/32 [110/128] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O 10.0.0.13/32 [110/129] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O N2 10.3.1.0/24 [110/20] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
O 10.1.0.1/32 [110/64] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
O*IA 0.0.0.0/0 [110/65] via 10.1.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial1/0
Configuring OSPF Flood Reduction
After the OSPF flood reduction is configured on the hub router, the OSPF database size on the spoke routers is reduced and they lose all OSPF routes:
Hub#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Hub(config)#interface serial 1/0
Hub(config-if)#ip ospf database-filter all out
Hub(config-if)#
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.11 on Serial1/0 from FULL to DOWN, →
Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.13 on Serial1/0 from FULL to DOWN, →
Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.12 on Serial1/0 from FULL to DOWN, →
Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.12 on Serial1/0 from LOADING to FULL, →
Loading Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.11 on Serial1/0 from LOADING to FULL, →
Loading Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.0.0.13 on Serial1/0 from LOADING to FULL, →
Loading Done
S1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (10.0.0.11) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
10.0.0.11 10.0.0.11 5 0x80000001 0x00C46A 4
S1#show ip route | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.11/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.2.11.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
Configuring Static Default Route on the Spoke Routers
Following the OSPF flood reduction configuration, the spoke routers no longer have connectivity beyond the directly-connected interface of the hub router. You have to configure a static default route pointing to the hub router on the spoke routers:
S1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
S1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.0.1
S1(config)#^Z
S1#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
S1#show ip route | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is 10.1.0.1 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.11/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.2.11.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.1.0.1
You can use ping on the spoke routers after you have configured static default routes to verify spoke-to-hub and spoke-to-spoke connectivity.
S1#ping 10.2.1.1 source FastEthernet 0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.2.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.2.11.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/101/228 ms
S1#ping 10.2.12.1 source FastEthernet 0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.2.12.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.2.11.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 128/208/304 ms
Router Configurations
upgrade fpd auto
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Hub
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
logging message-counter syslog
!
no aaa new-model
ip source-route
ip cef
!
no ip domain lookup
no ipv6 cef
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf network point-to-multipoint
ip ospf database-filter all out
serial restart-delay 0
cdp enable
frame-relay lmi-type ansi
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
area 1 nssa default-information-originate no-summary
network 10.1.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 1
network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
logging alarm informational
!
control-plane
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
no login
!
end
upgrade fpd auto
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname S1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
logging message-counter syslog
!
no aaa new-model
ip source-route
ip cef
!
no ip domain lookup
no ipv6 cef
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.0.0.11 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.2.11.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.1.0.11 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf network point-to-multipoint
serial restart-delay 0
cdp enable
frame-relay lmi-type ansi
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
area 1 nssa
network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 1
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.0.1
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
no login
!
end
